Medically review by Kim Langdon
In this post, you will learn about the vagus nerve: what it is, its impacts on our health, and why and how you can stimulate it for benefits like reducing inflammation and better memory.


So, what is the vagus nerve?
Vagus means "wandering" in Latin, which is also where we derive the word vagabond from.
You can think of this nerve as something like a traveler, considering it has multiple branches that wander all over the body.
It's the autonomic nervous system's longest nerve, and the autonomic nervous system is important for our “rest-and-digest” or “tend-and-befriend” responses.
Basically, it's the captain of the ship, and like with any leader, we're right to be concerned with what it does and how well it's doing the job - especially when it's all over the place!
It helps to deliver motor parasympathetic fibers to all the organs besides our adrenal glands, and it also controls a number of our skeletal muscles.
For our nervous system to be in tip-top shape, we need to know the inner workings of our vagus nerve.
Heart to heart
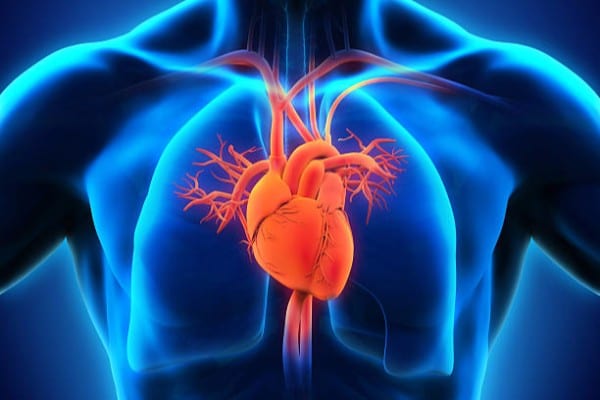

Let's begin with the important stuff! The heart is one of our body's most important organs because... well, it keeps us alive as long as it's pumping away.
The vagus nerve controls the heart rate by sending electrical impulses to the sinoatrial node, located in the heart.
Acetylcholine - a neurotransmitter we'll be talking a lot about in this article - releases and slows the pulse, which means the vagus nerve commands your heart rate.
Heart rate is actually one of the most accurate points of reference in gauging the overall health of the vagus nerve, so it's critical to understand the connection.
Vagus nerve's impact on obesity


The vagus nerve plays an important role in helping us feel satiated after a meal, which leads us to its link to obesity.
Essentially, it's responsible for sending that signal to stop eating when we're full to the brain, making it aware that we have short-term energy to use up.
This study indicates that the integrity of our vagal system could thus be linked to obesity.
If the vagus nerve is not functioning optimally, our hunger signals may not work to the best of their ability, causing overeating and weight gain.
It keeps you calm


Like the release of the stress hormone cortisol sends our bodies into "fight or flight" mode, the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the “rest-and-digest” mode.
The vagus nerve sends signals to release prolactin, vasopressin, and oxytocin - all of which calm us down.
Over time, a strong vagal tone can increase stress tolerance which will lead to faster recovery time from illness, injury, stress, and emotional trauma.
According to research, vagus nerve stimulation has promising results for quelling anxiety and fear - even when fear is too strong for exposure therapy.
It aids in memory formation


Research concludes that stimulating the vagus nerve releases norepinephrine into the amygdala and hippocampus - the parts of the brain that form memory.
As a result, they work harder to store memories, leading us to believe that the dramatic surge in norepinephrine is largely happening in our internal memory banks.
With additional studies - particularly those done on human subjects - we could potentially form a connection to vagal tone and Alzheimer's risk and treatment.
The vagus nerve & the brain-gut axis

No surprise here! We have yet another connection in the body to the gut - our body's other control center.
Intestinal permeability, gut bacteria, and overall gut health have a huge impact on our brain.
Studies show that gut microorganisms can activate the vagus nerve which impacts the brain and behavior.
One of those signals is an anti-inflammatory signal, releasing mediator acetylcholine.
Benefits of vagus nerve stimulation
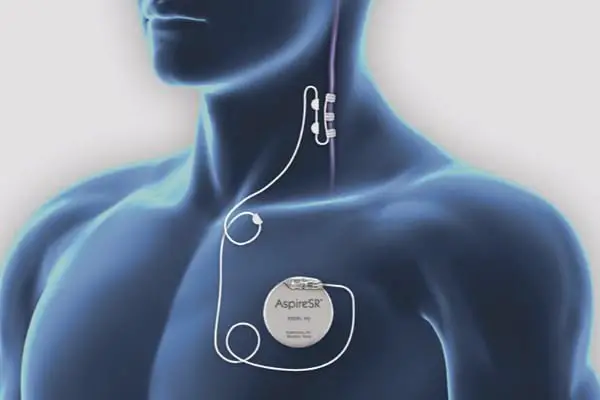

Vagus nerve stimulation is a medical procedure, during which electrical shocks are sent to the nerve, delivered through an implantation.
It's often used to treat epilepsy and depression that is unresponsive to typical treatment, but the scope of treatment is widening with new research that leads us to believe it could be beneficial to those who suffer from chronic inflammation.
The reason this works is that the electrical signals reach the brain stem where they have a perfect starting point to send signals to other parts of the brain.
The rationale behind its strong link to inflammation is linked to vagal tone. Like the heart, the "tone" or overall health of it matters, and it impacts many other bodily functions.
In one study, an upward-spiral dynamic was shown, linking positive emotion, social connection, and physical health - indicated by vagal tone.
People who want to get on board with this theory can increase positive emotion with loving-kindness meditation which helps people self-generate a positive attitude toward the self and others.
How to stimulate the vagus nerve


If you simply want to improve vagal tone and reap the benefits, you don't need an implant. Simple deep breathing exercises are enough to stimulate the nerve and slow the heart rate.
Acetylcholine tells the lungs to breathe quite literally, so without your vagus nerve, you'd stop the most essential part of your life force.
Deep diaphragmatic breathing with an emphasis on the exhale can reduce anxiety and stress, increasing heart rate during the inhale and decreasing it with the out-breath or exhale.
This is the simplest means of stimulation, and an easy exercise you can start with today. Meditation or yoga poses - both of which incorporate deep breathing - stimulate the vagus nerve.
According to this article, some of the other methods of activating or stimulating the vagus nerve include: cold showers, singing and chanting, gargling, fasting, tai chi, massages (yes please!), acupuncture and our favorite, laughter.
Research shows that those with more severe inflammation like an autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) could benefit greatly from an implant.
This is because cytokine levels, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and inflammation decrease. Cytokines are pro-inflammatory and may also induce depression and low energy.
This is promising because it offers a unique and holistic alternative to long-term medication to those with chronic pain, and is a huge breakthrough in the world of medicine.
This research has essentially created a new field of medicine altogether.
Finally, it's important to understand over-stimulation of the vagus nerve and vagus nerve damage.
During vagal syncope - times in which the nerve is experiencing too much stimulation - the brain experiences restricted blood flow which can lead to dizziness, weakness, or unconsciousness.
This can be a minor threat, especially if you're someone who, for example, gets queasy when you see blood. Often, you can just sit down and relax to ease the symptoms.
Other causes of vagus nerve dysfunction include IBS, weight gain, depression, and anxiety.
Can you tell we are quite excited about the breakthroughs in medicine regarding the vagus nerve?
This powerhouse system is truly a missing link, and we hope you learned something new in our feature today.
This article was fact checked for accuracy by Dr. Kim Langdon, MD. As always, this is not personal medical advice and we recommend that you talk with your doctor.
Share on Pinterest

Kimberly Langdon M.D. is a retired University-trained obstetrician/gynecologist with 19-years of clinical experience. She delivered over 2000 babies to mothers in a suburban Midwestern community.

